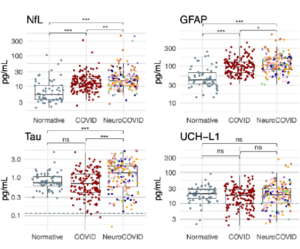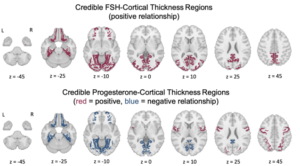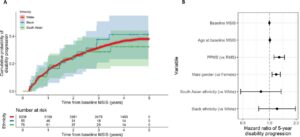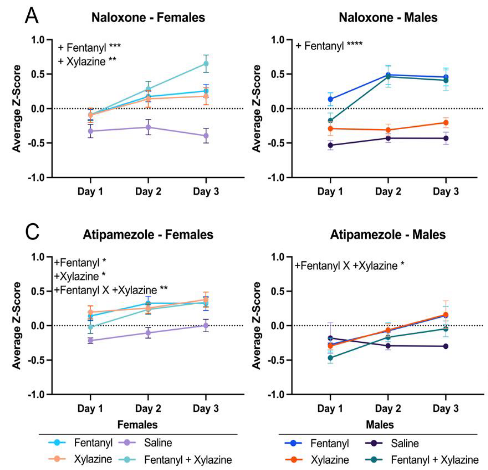
Madigan L. Bedard, et al. – UNC Chapel Hill.
In this study, Bedard and colleagues found that xylazine activates kappa opioid receptors (KORs) and, in female mice, is responsive to naloxone. Xylazine pharmacology, especially in the context of opioids and naloxone, is of growing importance for public health with the increased prevalence of fentanyl being adulterated with xylazine. Since xylazine’s known receptor is the alpha-2-adrenergic receptor (α2-AR), it has been believed, even by the DEA, that xylazine overdoses would not be responsive to naloxone.
While naloxone did not induce xylazine withdrawal in male mice, it did achieve this in female mice. Xylazine also enhanced the level of naloxone-induced withdrawal symptoms of fentanyl when the two were co-administered to female mice. These sex differences are likely due to known differences in the kappa-opioid and adrenergic systems. Intriguingly, the α2-AR antagonist atipamezole induced withdrawal symptoms after female mice were given unadulterated fentanyl, suggesting an interaction between the α2-AR and KOR pathways.