Erica Bello, et al. – Wellcome Sanger Institute.
Background: As with most putative AD risk loci, it is unclear whether variants of the PTK2B gene are causal.
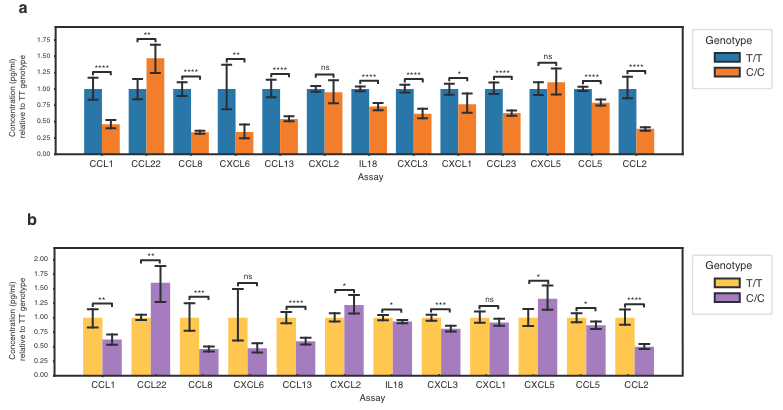
This Study: Bello and colleagues examined the role of a putative protective PTK2B variant, rs28834970 (T to C), using microglia derived from a human induced pluripotent stem cell (hIPSC) line engineered to carry the mutation. They found that this variant introduces an intronic binding site for the transcriptional repressor CEBPB, leading to reduced PTK2B expression. In line with known roles for PTK2B in promoting cell migration and chemokine expression, microglia bearing the protective variant produced lower levels of numerous chemokines, both at baseline and following stimulation with interferon gamma (IFNγ), and were less sensitive to the chemoattractant C5a and the chemorepellent IFNγ.
Bottom Line: rs28834970 represents a causal variant for reducing AD risk by curbing the inflammatory profile of microglia.