“Attenuating amyloid-beta pathology in mice with in situ programmed astrocytes.”
Lun Zhang, et al. – Chinese Academy of Sciences.
Background: Enhancing clearance of amyloid-β oligomers (AβOs) and restoring normal cytokine profiles could be effective in reducing AD pathology.
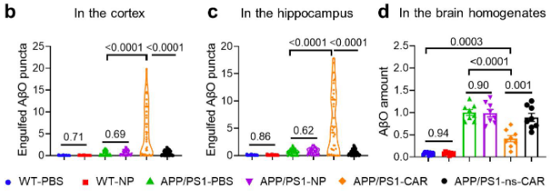
This Study: Zhang and colleagues designed an approach for generating chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) astrocytes (CAR-A), fusing an AβO-binding W20 domain to the MerTK receptor. Usage of MerTK couples phagocytosis of AβOs to the downregulation of pro-inflammatory cytokines and upregulation of anti-inflammatory ones, a benefit not observed in previous anti-amyloid CARs. Additionally, the vector for generating CAR-As is administered intranasally, providing a non-invasive and well-tolerated vehicle. In the APP/PS1 mouse model, CAR-A induction restored performance on 3 memory assays to levels approaching WT controls, reduced amyloid plaques, and shifted astrocytes & microglia towards homeostatic states.
Bottom Line: CAR-As could provide a non-invasive method for promoting AβO clearance, reducing neuroinflammation, and curbing gliosis to combat cognitive decline. This innovative technique for astrocyte programming may have many other applications if human studies bear out these results.