Brandon Buxton, et al. – Bronson Healthcare Group.
Background: Patients with MS frequently experience visual impairments (VIs). Predictive models using data sourced from electronic health records (EHRs) could aid in identifying those at risk for developing VIs for closer monitoring and more aggressive treatment.
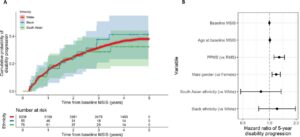
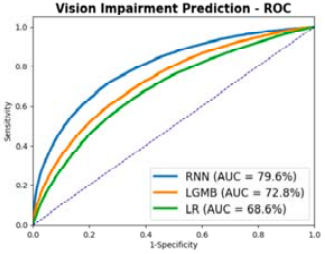
This Study: Using EHR data from Epic Cosmos, Buxton and colleagues compared the health trajectories of 42,281 patients with MS who developed VIs after their diagnosis with those of 334,816 patients without VIs. A recurrent neural network (RNN) trained on all patient data collected prior to the VI diagnosis achieved an AUROC of 0.796 for predicting VI status. An RNN, as well as logistic regression and light gradient boosting machine models, performed more modestly when only using data up to and including when patients were diagnosed with MS, with the RNN achieving an AUROC of 0.632.
Bottom Line: An RNN provides insights into whether patients who have experienced MS for a number of years will develop neurologically-mediated vision loss.